The Standard for Gas Mask has been enacted as follows conforming to and
in order to enforce the Industrial Safety and Health Law (Law No. 57 of
1972).
Contents
(Scope of application)
Article 1
The standard issued in the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare Notification
is applied to the gas masks which are categorized into those described
in the left column of the following Table, according to the kinds of hazardous
materials (including particulates which coexist with these gaseous materials)
described in the right column of the same Table, among the gas masks to
be used at the places where gases, vapors and particulates mixed with these
gases or vapors may harm the human body by inspiring them. However, this
standard is not applied to those gas masks used in places where oxygen
concentration is below 18% or the concentrations of gases or vapors exceeds
2% ( in case the gas is ammonia, the concentration exceeds 3%).
|
Category
|
Hazardous materials
|
|
Gas masks for halogens
|
Halogen gases or vapors
|
|
Gas masks for organic compounds
|
Organic compound vapors
|
|
Gas masks for carbon monoxide
|
Carbon monoxide
|
|
Gas masks for ammonia
|
Ammonia
|
|
Gas masks for sulfur dioxide
|
Sulfur dioxide
|
(Type of gas mask)
Article 2
Gas masks shall be categorized into the types described in the left column
of the following Table, according to the form and the scope of application
described in the right column of the same Table.
|
Type
|
Form and scope of application
|
|
Front or back mounted type gas mask
|
It is composed of a canister, a breathing tube, inhalation valve(s), a facepiece,
exhalation valve(s), and head harness. Clean air filtered
by the canister is inhaled from the inhalation valve(s) through the
breathing tube , and exhaled air is exhausted from the exhalation valve(s)
to outside atmosphere, and is used in the atmosphere where the concentration
of the gases or vapors is less than 2 % (3 % for ammonia).
|
|
Chin -style gas mask
|
It is composed of canister(s), inhalation valve(s), a facepiece, exhalation
valve(s) and head harness. Clean air filtered by the canister(s)
is inhaled from the inhalation valve(s), and exhaled air is exhausted
from the exhalation valve(s) to outside atmosphere, and is used in the
atmosphere where the concentration of the gases or vapors is less than
1 % (1.5 % for ammonia).
|
|
Chemical cartridge respirator
|
It is composed of chemical cartridge(s), inhalation valve(s), a facepiece,
exhalation valve(s) and head harness. Clean air filtered by the cartridges(s)
is inhaled from the inhalation valve(s), and exhaled air is exhausted from
the exhalation valve(s) to outside atmosphere. It is used in the atmosphere
where the concentration of the gases or vapors is less than 0.1 %, and
is not used for emergency.
|
2 Facepiece of gas masks shall be categorized into the types described
in the left column of the following Table, according to the form described
in the right column of the same Table.
|
Type
|
Form
|
|
Full-face facepiece
|
It covers whole face.
|
|
Half mask facepiece
|
It covers only nose and around mouth.
|
3 Gas masks shall be categorized into types with and without the function
to filter particulate contaminants, and the gas masks with the function
to filter particulates shall be categorized into S1, S2, S3, L1, L2, and
L3, according to its performance.
(Materials)
Article 3
The materials to be used for each part of gas masks shall conform to the
requirements described in the following each item.
1. The material used at the part tightly contacted with face must give
no harm to the skin.
2. The inside of the gas filter must be composed of the material which
is not corroded by filter material or must be surface-treated enough so
that it is not corroded by filter material.
3. The filter material must give no harm to human body.
4. The material used must be strong enough not to be defected to give tear
or distortion by ordinary application.
(Test on strength)
Article 4
The individual part of gas masks shall conform to the requirements
described in the right column of the following Table, when it is submitted
to the tests described in the middle column of the same Table, according
to the parts described in the left column of the same Table.
|
Parts
|
Tests
|
Requirements
|
|
Head harness and its mounting base of the facepiece
|
(Pulling Test)
Each combination of head harness and its mounting base of the facepiece
is pulled with tension force of 50 Newton for full-face type facepiece,
with tension force of 25 Newton for half mask facepiece, and investigated
whether breakage or separation is caused.
|
Breakage or separation on both parts must not be caused.
|
|
Breathing tube of front or back mounted type gas mask and its mounting
base of the facepiece
|
(Pulling Test)
Breathing tube and its mounting base of facepiece is pulled by the force
of 98 Newton.and investigated whether breakage or separation is caused
|
Breakage or separation on both parts must not be caused.
|
(Structure)
Article 5
The structure of gas masks shall conform to the requirements shown in
the following each item.
1. It must be not easy to break.
2. It must be easy to wear, and not to give a pressed feeling or pain
when being worn.
3. The dead space must not be too large.
4. It must not remarkably narrow the visual field of the wearer.
5. The gas mask having full-face type facepiece should not be dimmed at
eyepiece(s) by exhalation.
6. Those gas masks having replaceable canister(s) or cartridge(s), inhalation
valve(s), exhalation valve(s) or head harness should be so designed that
those replaceable parts are easily replaced.
7. The air tightness between face and facepiece can be easily checked
anytime by wearers themselves.
Article 6
The structure of individual part of gas masks shall conform to the requirements
described in the right column of the following Table, according to the
parts described in the left column of the same Table.
|
Part
|
Requirements
|
|
Gas filter
(Canister and Chemical cartridge
|
1. Filter material must
be packed tightly and not exposed to outside.
2. It must be provided with
filter material to capture particulates, if the gas mask has the function to prevent wearer's exposure to particulates.
|
|
Inhalation valve
|
It must work reliably and quickly even for weak breathing.
|
|
Exhalation valve
|
1. It must work reliably
and quickly even for weak breathing, at both wet and dry conditions of the valve and the valve seat.
2. When the inside and outside
pressures of the gas mask is in equilibrium, the exhalation valve must be kept close tightly, whichever the facepiece is
directed to.
3. It must be protected
by cover or alike measures so that damage is not caused by forces given from outside.
|
|
Head harness
|
1. It must have appropriate
length and elasticity, and the length of harness must be easily adjusted.
|
|
Breathing tube
|
1. It must have appropriate
elasticity for expansion and contraction of length, and must cause no inconvenience in airflow when it is bent into variety of
forms.
2. It must cause no problem
in airflow when it is pressed by chin or arm.
3. The length must be long
enough to cause no restriction of head movement.
|
(Performance tests)
Article 7
The performance of gas mask (except canisters and cartridges) shall conform
to the requirements described in the right column of the following Table
when it is tested by the test procedures described in the left column of
the same Table.
|
Test procedures
|
Requirements
|
|
(Test of air tightness)
The air tightness of front or back mounted type gas masks, chin-style gas
masks and chemical-cartridge respirators, is tested as follows. First,
the exhalation valve(s) and the other end of a breathing tube connecting
to the facepiece are closed for a front or back mounted type, or the exhalation
valve(s) and the connection port(s) of a facepiece for canister(s) or cartridge(s)
are closed respectively by putting a sealing piece(s), and then the facepiece
is mounting onto a dummy head of the tightness test equipment. The facepiece
is covered with a cloth wetted with an alcohol solution of phenolphthalein.
Then, by sending air containing ammonia into the facepiece until the inside
pressure reaches at 980 Pascal, color change of the cloth into red is investigated
to find the parts where the air tightness is broken on the facepiece.
|
No leakage shall be detected.
|
|
(Test of inhalation resistance)
This test measures the difference between inner and outer pressure of the
facepiece putted on a dummy head during passing airflow at the rate of
40 liters per minute in the direction of inhalation. In this test, the
canister(s) or cartridge(s) ( involving inhalation valve(s) when the inhalation
valves are attached to the canister(s) or cartridges(s)) are removed from
the facepiece. When the gas mask has a breathing tube, the pressure difference
is measured with the tube bent at 180 degree.
|
The pressure difference shall not exceed 70 Pascal for front or back mounted
type gas masks, and 50 Pascal for chin-style gas masks and chemical cartridge
respirators, respectively.
|
|
(Test of exhalation resistance)
This test measures the difference between inner and outer pressure of the
facepiece putted on a dummy head during passing airflow at the rate of
40 liters per minute in the direction of exhalation. In this test, the
air passes for inspiration should be closed.
|
The exhalation resistance shall not exceed 80 Pascal
|
|
(Test of air tightness of exhalation valve at work)
First, the exhalation valve with the valve seat is mounted on an air tightness
test equipment, and then the decrease of the inner pressure of the valve
is confirmed by drawing the inside air by a drawing pump at the rate of
1 liter per minute. Next, the inner pressure is adjusted at –1,470
Pascal against the atmospheric pressure, then the evacuation of the inner
space of the valve is stopped, and then the time for the inner pressure
to recover to the atmospheric pressure is measured. The capacity of the
inner space of the exhalation valve seat shall be 50 cubic centimeters.
|
1. The inner pressure must quickly decrease when the inner air is drawn.
2. The time required for the inner pressure to be restored up to normal
pressure must be longer than 15 seconds.
|
|
(Test of carbon dioxide concentration increase in inspired air)
In the atmosphere of 25 ± 5°C , the facepiece is put on a dummy
head with the dimensions described in the following picture, and the connected
artificial breathing apparatus is driven at the rate of 15 times a minute
and 2.0 ±0.1 liters per stroke (The artificial breathing apparatus
supplies exhalation air with 5.0% carbon dioxide.). During this procedure,
the carbon dioxide concentration in the inspired air is measured until
the concentration reaches a constant concentration. The same procedure
is performed with the dummy head without a facepiece.
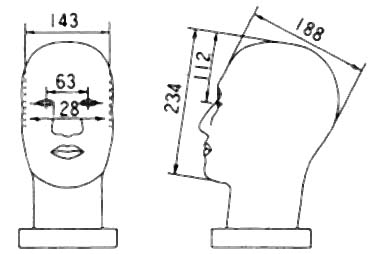
Dummy Head (in mm)
|
The difference of carbon dioxide concentrations in the inspired air at
the two conditions with and without the facepiece must be lower than 1.0%.
|
2 The performance of canisters and cartridges shall conform to the requirements
described in the right column of the following Table when tested by the
test procedures described in the left column of the same Table.
|
Test procedures
|
Requirements
|
|
(Test of air-tightness)
This test investigates whether leakage is found or not after sending air
into the canister or cartridge until the pressure in the canister or cartridge
reaches at 1470 Pascal.
|
No leakage shall be detected.
|
|
(Test of inhalation resistance)
This test measures the difference between the pressures of the air flow
before and after it passes through a canister or a cartridge at the rate
of 40 liters per minute. The canister or cartridge to which an inhalation
valve is attached is measured with the valve.
|
The pressure difference shall not exceed the values described in the Table
below, according to the type of the gas mask to which the canister or cartridge
is connected and with or without the function of filtration of particulates.
|
|
Category
|
Type of gas mask
|
Front or back mounted type gas mask
|
Chin-style gas mask
|
Chemical-cartridge respirator
|
|
For carbon monoxide
|
With particulate filtration function
|
S1 &L1
|
310
|
-
|
-
|
|
S2 &L2
|
320
|
-
|
-
|
|
S3 &L3
|
400
|
-
|
-
|
|
Without particulate
filtration function
|
280
|
-
|
-
|
|
For gases other than carbon monoxide
|
With particulate filtration function
|
S1 &L1
|
310
|
280
|
280
|
|
S2 &L2
|
320
|
290
|
290
|
|
S3 &L3
|
400
|
370
|
370
|
|
Without particulate filtering function
|
250
|
220
|
220
|
|
Remark: The value in this Table is in the unit of Pascal.
|
|
Test procedures
|
Requirements
|
|
(Test of service life)
Service life is measured, by supplying air containing the gas shown in the
right column of the Table below into the canister or the cartridge,
at the flow rate of 30 liter per minute, according to the type of the
canister or cartridge shown in the left column of the same Table.
During the testing, the temperature and the relative humidity shall be,
respectively, 20 °C±
2 °C and
50% ± 5%.
1. The case where a gas
analyzer is used;
The air flow containing the test gas at the exit of the gas filter, which
has passed through the gas filter, is led into the gas analyzer, and then
the concentration of the test gas in the effluent is measured.
2. The case where gas absorption method is applied;
The air flow containing the test gas at the exit of the gas filter, which
has passed through the gas filter, is led into the absorbing tube containing
absorbing liquid, and then the test gas contained in the test air is absorbed,
and the concentration of the test gas is measured.
|
The time required for the exit gas to reach at the concentration shown
in the middle column of the Table below shall be longer than the time shown
in the right column of the same Table, according to the kind of canister
and cartridge shown in the left column of the same Table.
However, in the case of canister of front or back mounted type gas mask
for carbon monoxide which shows an initial leakage of carbon monoxide within
5 minutes from the start of the test, the concentration of the test gas
which has passed through the canister shall not exceed 100 ppm within 5
min from the start of the test due to no reaction or no absorption.
|
|
Type of gas filter
|
Test gas
|
Type of gas filter
|
Concentration
(ppm)
|
Time
(min)
|
|
Kind
|
Concentration
|
|
Canister of front or back mounted type gas mask for halogens
|
Chlorine
|
0.5%
|
Canister of front or back mounted type gas mask for halogens
|
1
|
60
|
|
Canister of chin-style gas mask for halogens
|
Chlorine
|
0.3%
|
Canister of chin-style gas mask for halogens
|
1
|
15
|
|
Cartridge of chemical cartridge respirator for halogens
|
Chlorine
|
0.02%
|
Cartridge of chemical cartridge respirator for halogens
|
1
|
40
|
|
Canister of front or back mounted type gas mask for organic vapors
|
Cyclo hexane
|
0.5%
|
Canister of front or back mounted type gas mask for organic vapors
|
5
|
100
|
|
Canister of chin-style gas mask for organic vapors
|
Cyclo hexane
|
0.3%
|
Canister of chin-style gas mask for organic vapors
|
5
|
30
|
|
Cartridge of chemical cartridge respirator for organic vapors
|
Cyclo hexane
|
0.03%
|
Cartridge of chemical cartridge respirator for organic vapors
|
5
|
50
|
|
Canister of front or back mounted type gas mask for carbon monoxide
|
Carbon monoxide
|
1.0%
|
Canister of front or back mounted type gas mask for carbon monoxide
|
5
|
180
|
|
Canister of front or back mounted type gas mask for ammonia
|
Ammonia
|
2.0%
|
Canister of front or back mounted type gas mask for ammonia
|
50
|
40
|
|
Canister of chin-style gas mask for ammonia
|
Ammonia
|
1.0%
|
Canister of chin-style gas mask for ammonia
|
50
|
10
|
|
Cartridge of chemical cartridge respirator for ammonia
|
Ammonia
|
0.1%
|
Cartridge of chemical cartridge respirator for ammonia
|
50
|
40
|
|
Canister of front or back mounted type gas mask for sulfur dioxide
|
Sulfur dioxide
|
0.5%
|
Canister of front or back mounted type gas mask for sulfur dioxide
|
5
|
50
|
|
Canister of chin-style gas mask for sulfur dioxide
|
Sulfur dioxide
|
0.3%
|
Canister of chin-style gas mask for sulfur dioxide
|
5
|
15
|
|
Cartridge of chemical cartridge respirator for sulfur dioxide
|
Sulfur dioxide
|
0.03%
|
Cartridge of chemical cartridge respirator for sulfur dioxide
|
5
|
35
|
|
Remark: The unit ppm in this Table shows one millionth in volume.
|
|
(Test of particulate filtering efficiency)
For the gas masks with the function of particulate filtration, the particulate
filtering efficiency is measured by the measurements of the particle
concentration of the test air flow before and after it passes the canister
or cartridge incorporating the particulate filter, and by the succeeding
calculation in use of the following equation. The particles
used for the test of particulate filtering efficiency is either of the
following two kinds chosen depending on the kind of the particulate
filter. The particle size distribution of the test particles
is represented by the count median diameter.
Particulate filtering efficiency (%) =
Concentration before passing -
(mg/cubic meter) |
Concentration after passing
(mg/cubic meter) |
X 100 |
 |
Concentration before passing
(mg/cubic meter) |
|
|
|
1. The case where the test particle is sodium chloride;
The concentrations of sodium chloride in the test flow before and after
passing through the gas filter are continuously measured with a sodium
chloride concentration measuring instrument with the light scattering method.
The count median diameter of the particle size of sodium chloride shall
be from 0.06 micrometer to 0.10 micrometer and the geometrical standard
deviation of the particle size distribution shall be less than 1.8. The
air flow containing sodium chloride at the concentration lower than 50
mg per cubic meter with the variation range less than 15% is made pass
through the canister or the cartridge at the flow rate of 85 liters per
minute until the cumulative sodium chloride supplied to the filter reaches
at 100mg. The particulate filtering efficiency is calculated for the maximum
concentration of sodium chloride in the air flow downward the canister
or the cartridge during the test.
|
|
1. The case where the test particle is sodium chloride;
The particulate filtering efficiency of the canister or the cartridge through
the test duration shall exceed the value described each in the right column
of the Table below, according to the type of the canister or the cartridge
described in the left column of the same Table.
|
|
|
Type
|
Particulate filtering efficiency (%)
|
|
S1
|
80.0
|
|
S2
|
95.0
|
|
S3
|
99.9
|
|
2. The case where the test particle is dioctyl phthalate;
The concentrations of dioctyl phthalate in the test flow before and after
passing through the canister or the cartridge are continuously measured
with a dioctyl phthalate concentration measuring instrument with the light
scattering method. The count median diameter of the particle size of dioctyl
phthalate shall be from 0.15 micrometer to 0.25 micrometer and the geometrical
standard deviation of the particle size distribution shall be less than
1.6. The air flow containing dioctyl phthalate at the concentration lower
than 100 mg per cubic meter with the variation range less than 15% is made
pass through the canister or the cartridge at the flow rate of 85 liters
per minute until the cumulative dioctyl phthalate supplied to the filter
reaches at 200mg. The particulate filtering efficiency is calculated for
the maximum concentration of dioctyl phthalate after passing the canister
or the cartridge during the test.
|
2. The case where the test particle is dioctyl phthalate;
The particulate filtering efficiency during the test duration shall be
exceeding the value described each in the right column of the Table below,
according to the type of the gas filter described in the left column of
the same Table.
|
|
Type
|
Particulate filtering efficiency (%)
|
|
L1
|
80.0
|
|
L2
|
95.0
|
|
L3
|
99.9
|
(Labeling and others)
Article 8
Gas mask (except canister and cartridge) must be attached with a printed
matter describing the items shown below.
1. Name of manufacturer
2. Name of Type
3. Remarks in application
4. For the Type in which canister(s) or cartridge(s) can be replaceable,
the kind of the canister or the cartridge, its Type name and the Certificate
number of the canister or the cartridge which can be attached to the gas mask.
2 Canister and cartridge (For those which incorporate particulate filters
separable from the gas filters, both gas filter and particulate filter
in separation) shall be labeled at easily observable place on the surface,
describing the manufacturer's name and the manufactured year and month.
3 Canister and cartridge must be attached with a printed matter describing
the items shown below.
1. Name of Type
2. Scope of application
3. Remarks in application
4. Chart of breakthrough time curve
5. Record card for service time
6. Increased value of inhalation resistance ( only for gas mask having
particulate filtering function)
7. Procedure for the wearer easily to check the air tightness
between face and facepiece
4 The increased value of inhalation resistance specified in Item 6 of Part
3 of this Article shall be measured as the value of difference between
inner and outer pressure of the test air flow at 40 liters per minute when
100 mg of cumulative sodium chloride is supplied to the gas filter for
the particulate filtering efficiency test.
5 The outer side face of a gas filter shall be colored as described in
the right column of the Table below, according to the type of the gas filter.
|
Type
|
Color
|
|
Gas filter for halogens
|
Grey and Black (to be shown by two layers)
|
|
Gas filter for organic vapors
|
Black
|
|
Gas filter for carbon monoxide
|
Red
|
|
Gas filter for ammonia
|
Green
|
|
Gas filter for sulfur dioxide
|
Orange
|
|
Remark: For gas mask having particulate filtering function, a white line
on the side face of the canister or cartridge shall show the location of
the filter incorporated within the canister or cartridge.
|
(Exceptions of this Standard)
Article 9
The provisions issued by this official announcement are not applied for
those gas masks for which material, structure or performance is special,
or which is used at special conditions, and to which application of the
provisions shown in Article 1 through Article 7 is not appropriate only
when the Director General of Labour Standards Bureau of the Ministry of
Health, Labour and Welfare accepts that the gas mask has equivalent to
or better effectiveness than the gas masks conforming to this standard.
