
Outline of
"The Institute for Safety and Health Qualifying Examination"
(Testing institution designated by the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare)
|
- An Industrial Safety and Health Law stipulates the following articles about
the license examination related to Safety and Health.
- Article 75.
1. The license examination shall be conducted, for each classification
as provided for by Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare Ordinance, by
the Director General of the Prefectural Labour Bureau.
Article
75-2.
1. The Minister of Health, Labour and Welfare may, as provided for by Ministry
of Health, Labour and Welfare Ordinance, entrust the execution implementation
of the whole or part of the business of carrying out the license examination
to be conducted by the Director General of the Prefectural Labour Bureau
under the provisions of paragraph 1 of the Article 75 (hereinafter referred
to as the "test business") to one designated by the Minister
of Health, Labour and Welfare (hereinafter referred to as the "designated
testing institution").
"The Institute for Safety and Health Qualifying Examination"
is the "designated testing institution" provided by Article 75-2.
|
Objectives and Overview of the Institute for Safety and Health Qualifying
Examination
- This institute implements the following examinations on behalf of the national government by designation of the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare.
- License examinations for boiler operators, crane operators, health officers,
diving workers, etc., under the Industrial Safety and Health Law.
-
Examinations for industrial safety consultants and industrial health consultants
under the same law.
- Examinations for working environment measurement experts under the Working
Environment Measurement Law.
 Location: Location:
- Suidobashi Building, 1-3-12 Misaki-cho, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo, 101-0061 JAPAN
TEL: 03-3295-1088
FAX: 03-3295-0809
 Date of Establishment: Date of Establishment:
- April 1, 1976
 Regional Centers: Regional Centers:
- Safety and Health Technical Centers (seven blocks nationwide)
 Competent Authorities: Competent Authorities:
- The Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare
- Organization of the Institute for Safety and Health Qualifying Examination
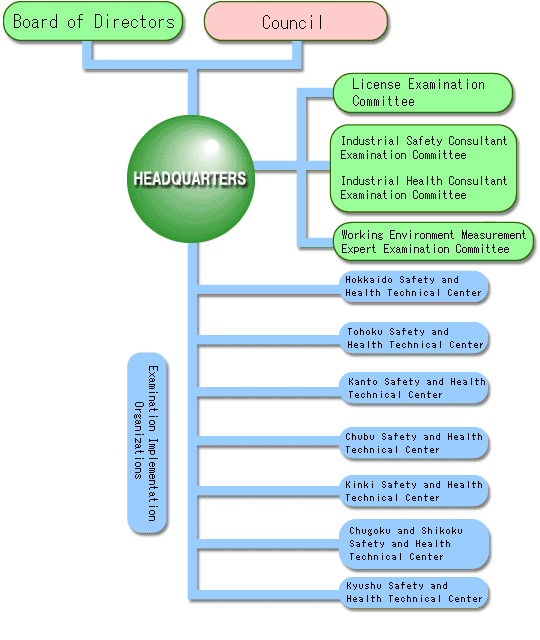
- Types of License Examinations
|
|
License Examinations |
| License Examinations Related to Safety |
License Examinations Related to Industrial Health |
|
|
Examinations for Industrial Safety Consultants
Examinations for Industrial Health Consultants |
|
|
| Examinations for Working Environment Measurement Experts |
|
|
| * Please Click the name of the lincense in the tree chart below. |
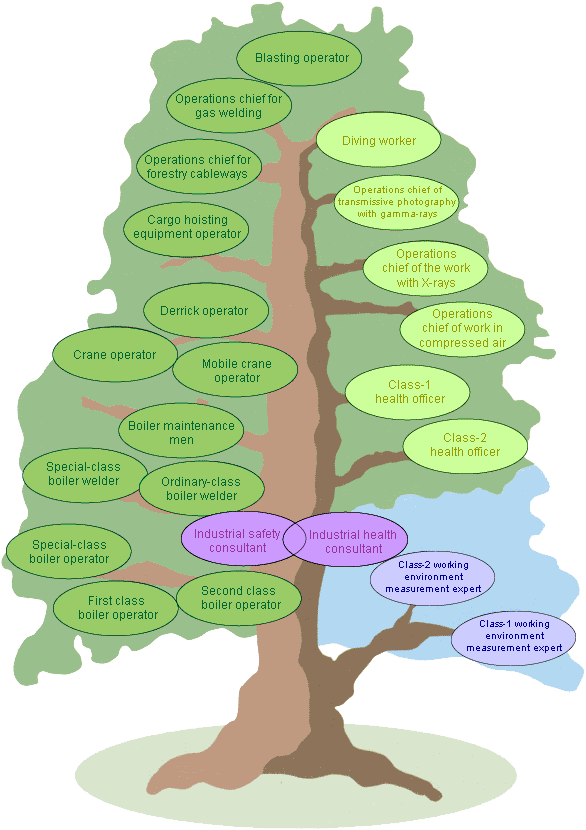
|
| License Examinations Related to Safety |
-
- (1) Boiler Operators (Special Class, First class, Second class)
- Boilers that are larger than a specified scale must be handled by licensed boiler operators. According to the heating surface of the boiler handled, operations chiefs who have special class, First class or Second class qualifications must be appointed. Boiler operators manage various boilers that constitute the energy source for factories, schools, hospitals, high-rise buildings, etc.
(Major Requirements for Test Taking)
Special Class:
Those with five years or more of experience in handling boilers (excluding small-sized boilers and compact boilers) after receiving a first class boiler operator license, or those with three years or more of experience as an operations chief for handling boilers after receiving a First class boiler operator license.
First class:
Those with two years or more of experience in handling boilers (excluding small-sized boilers and compact boilers) after receiving a Second class boiler operator license, or those with one year or more of experience as an operations chief for handling boilers after receiving a Second class boiler operator license.
Second class:
 Those who have completed the boiler practical training designated by the Director General of the Prefectural Labour Bureau. Those who have completed the boiler practical training designated by the Director General of the Prefectural Labour Bureau.
 Those who have graduated from universities, senior technical colleges,
or high schools with training in boiler-related courses, and who have completed
practical training based on the standards stipulated for handling boilers. Those who have graduated from universities, senior technical colleges,
or high schools with training in boiler-related courses, and who have completed
practical training based on the standards stipulated for handling boilers.
(2) Boiler Welders (Special Class, Ordinary Class)
- (*Practical skills examination is included.)
These qualifications are required for manufacturing, remodeling, and repairing boilers or Class-1 pressure vessels that are manufactured by welding. While special class boiler welders can handle all types of boilers, boilers that can be handled by ordinary class boiler welders are limited to those whose walls are no more than 25mm in thickness.
(Major Requirements for Test Taking)
Special Class:
Those with one year or more of experience in welding work for boilers or Class-1 pressure vessels after receiving a license for ordinary class boiler welders (excluding gas welding and automated welding)
Ordinary Class:
Those with one year or more of experience in welding work (excluding gas welding and automated welding)
- (3) Boiler Maintenance Men
- These qualifications are required by those who engage in the maintenance of the main units and peripheral equipment of boilers above a specified scale or Class-1 pressure vessels after discharging boiler water, etc.
(Major Requirements for Test Taking)
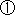 Those with six months or more of experience in assisting in the performance of maintenance work for boilers (excluding compact and small sized boilers) and Class-1 pressure vessels (excluding compact Class-1 pressure vessels and small sized pressure vessels). Those with six months or more of experience in assisting in the performance of maintenance work for boilers (excluding compact and small sized boilers) and Class-1 pressure vessels (excluding compact Class-1 pressure vessels and small sized pressure vessels).
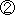 Those with six months or more of experience in the maintenance of compact boilers or compact Class-1 pressure vessels. Those with six months or more of experience in the maintenance of compact boilers or compact Class-1 pressure vessels.
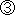 Those who have completed the boiler operation course from among the occupational training programs based on the Human Resources Development Promotion Law. Those who have completed the boiler operation course from among the occupational training programs based on the Human Resources Development Promotion Law.
- (4) Crane Operators
- (*Practical skills examination is included.)
These qualifications are required to operate various types of cranes with a lifting load of 5 tons or more, such as overhead cranes, bridge cranes and jib cranes. Cranes are widely used at factories, warehouses and construction sites.
(Major Requirements for Test Taking)
No special requirements are applied.
- (5) Mobile Crane Operators
- (* Practical skills examination is included.)
These qualifications are required to operate mobile cranes with a lifting load of 5 tons or more, such as truck cranes, rough terrain cranes, crawler cranes, and floating cranes. Mobile cranes are widely used at construction sites and harbors.
(Major Requirements for Test Taking)
No special requirements are applied.
- (6) Derrick Operators
- (* Practical skills examination is included.)
These qualifications are required to operate derricks with a lifting load of 5 tons or more, such as guy derricks, stiff-leg derricks and gin pole derricks. Derricks are used at civil engineering and construction work sites, etc.
(Major Requirements for Test Taking)
No special requirements are applied.
(7) Cargo Hoisting Equipment Operators
- (* Practical skills examination is included.)
These qualifications are required to operate cargo hoisting equipment with a limited load of 5 tons or more. Cargo hoisting equipment refers to derricks and cranes installed on ships, and is used for work at harbors to load and unload cargo from ships.
(Major Requirements for Test Taking)
No special requirements are applied.
- (8) Blasting Operators
- Qualifications required for blasting work at civil engineering work sites, etc.
Blasting work that uses explosives consists of punching, loading, wiring, ignition and post-blast processing. As this series of operations is accompanied by major danger, those who engage in blasting work must have qualifications designated by the national government.
Blasting operators work as special engineers who directly engage in blasting work at civil engineering and quarrying sites.
(Major Requirements for Test Taking)
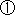 Those who have completed the practical training course on blasting as designated by the Minister of Health, Labour and Welfare. Those who have completed the practical training course on blasting as designated by the Minister of Health, Labour and Welfare.
 Those with 6 months or more of experience in assisting blasting work. Those with 6 months or more of experience in assisting blasting work.
 Those who have studied applied chemistry, mine engineering and civil engineering at universities, senior technical colleges or high schools, followed by three months or more of on-the-job training in blasting work after graduation. Those who have studied applied chemistry, mine engineering and civil engineering at universities, senior technical colleges or high schools, followed by three months or more of on-the-job training in blasting work after graduation.
- (9) Operations Chiefs for Gas Welding
Operations chiefs for gas welding must be appointed from among those licensed as operations chiefs for gas welding when welding, melt-cutting or heating work is carried out by using acetylene welding equipment or welding equipment using gas manifold.
Operations chiefs perform such duties as determining work methods and supervising workers, and assume responsibility for the entire work process.
(Major Requirements for Test Taking)
 Those who have completed the skills training course on gas welding and with three years or more of experience in work related to gas welding. Those who have completed the skills training course on gas welding and with three years or more of experience in work related to gas welding.
 Those who have studied subjects relating to welding at universities or senior technical colleges and graduated from such universities or senior technical colleges. Those who have studied subjects relating to welding at universities or senior technical colleges and graduated from such universities or senior technical colleges.
 Those who have studied engineering or chemistry at universities or senior technical colleges, and with one year or more of experience in work related to gas welding after graduation. Those who have studied engineering or chemistry at universities or senior technical colleges, and with one year or more of experience in work related to gas welding after graduation.
(10) Operations Chiefs for Forestry Cableways
Timber felled in mountains and forests is transported to collection sites by using skyline logging cable cranes and logging cableways. For work to assemble and disassemble skyline logging cable cranes and logging cableways as well as for yarding and logging work using such equipment, operations chiefs for forestry cableways must be appointed from among those licensed as operations chiefs for forestry cableways.
Operations chiefs perform such duties as determining work methods and supervising workers in assembling, maintaining and disassembling such equipment and in actual yarding and logging work.
(Major Requirements for Test Taking)
Those with three years or more of experience in forestry cableway work.
| License Examinations Related to Industrial Health |
-
- (1) Health Officers (Class-1 and Class-2)
- Persons promoting industrial health management at workplaces
Workplaces with 50 or more regular workers must appoint more than the prescribed number of health officers according to the number of workers. These appointments shall be limited to those licensed as health officers for the management of technical matters relating to health from among safety and health work.
While those with Class-1 health officer licenses can be health officers at workplaces of all types of businesses, those
with Class-2 health officer licenses can serve as health officers only at certain types of workplaces that
have little relationship with harmful work.
Major duties include working environment management and work management to prevent worker health impairment and the improvement of working conditions and facilities that are necessary for health management.
(Major Requirements for Test Taking)
 Those who have graduated from universities or senior technical colleges, and with one year or more of experience in practical work related to industrial health. Those who have graduated from universities or senior technical colleges, and with one year or more of experience in practical work related to industrial health.
 Those who have graduated from high schools, and with three years or more of experience in practical work related to industrial health. Those who have graduated from high schools, and with three years or more of experience in practical work related to industrial health.
 Those with ten years or more of experience in practical work related to industrial health. Those with ten years or more of experience in practical work related to industrial health.
- (2) Operations Chiefs of Work in Compressed Air
Operations chiefs of work in compressed air must be appointed for each work room from among those with licenses as operations chiefs of work in compressed air. Such persons shall be directly responsible for the prevention of high-pressure malfunctions when conducting work in high-pressure rooms (limited to work conducted in a room or inside a shaft where the pressure exceeds atmospheric pressure due to a caisson or other compressed air methods). Operations chiefs perform such duties as determining work methods and supervising workers.
(Major Requirements for Test Taking)
Those with two years or more of experience in work in high-pressure rooms
- (3) Operations Chiefs of the work with X-Rays
- Direct supervisors for work to conduct non-destructive X-ray testing
When conducting work using X-ray equipment (excluding medical equipment and the equipment with a rated tube voltage of 1,000 kV or more at peak value), operations chiefs of the work with X-rays must be appointed for each controlled area from among those licensed as operations chiefs of the work with X-rays. Such persons shall be directly responsible for the prevention of impairments due to X-rays. Operations chiefs perform such duties as determining work methods and supervising workers.
(Major Requirements for Test Taking)
No special requirements are applied.
- (4) Operations Chiefs of Transmissive Photography of Gamma-Rays
- Direct supervisors for gamma-ray welding inspections
In taking photographs using the gamma-ray irradiation equipment, operations chiefs of transmissive photography with gamma-rays must be appointed for each controlled area from among those licensed as operations chiefs of transmissive photography with gamma-rays. Such persons shall be directly responsible for the prevention of impairments due to gamma rays. Operations chiefs perform such duties as determining work methods and supervising workers.
(Major Requirements for Test Taking)
No special requirements are applied.
- (5) Diving Workers
Licenses are required for diving workers as diving work that uses diving equipment to receive air supplies from hand pumps or pressurized cylinders presents major dangers in terms of high-pressure injuries and other risks.
Venues in which diving workers can display their special skills include civil engineering work in the sea, salvage work, and gathering marine products. These venues are expanding to include new fields such as ocean development.
(Major Requirements for Test Taking)
No special requirements are applied.
| Examinations for Working Environment Measurement Experts |
- Working Environment Measurement Experts (Class-1, Class-2)
Experts in the maintenance and management of working environments
Only working environment measurement experts can measure the working environment in workplaces where organic solvents, specified chemical substances, radioactive substances, mineral dust and metals are handled.
Upon registration with the Minister of Health, Labour and Welfare, working environment measurement experts promote the maintenance and management of working environments at workplaces, thereby contributing to the maintenance of worker health.
There are two types of working environment measurement experts:
- Class-1 measurement experts can handle all aspects of design, sampling
and analyses (including mathematical analyses).
- Class-2 measurement experts can handle design, sampling and analyses using
simplified measurement devices only.
(Major Requirements for Test Taking)
 Those who have graduated in the sciences from universities or senior technical colleges and with one year or more of experience (three years or more for those who have graduated in non-science fields) in practical work related to industrial health. Those who have graduated in the sciences from universities or senior technical colleges and with one year or more of experience (three years or more for those who have graduated in non-science fields) in practical work related to industrial health.
 Those who have graduated in the sciences from high schools and with three years or more of experience (five years or more for those who have graduated in non-science fields) in practical work related to industrial health. Those who have graduated in the sciences from high schools and with three years or more of experience (five years or more for those who have graduated in non-science fields) in practical work related to industrial health.
 Those with eight years or more of experience in practical work related to industrial health. Those with eight years or more of experience in practical work related to industrial health.
Examinations for Industrial Safety Consultants
Examinations for Industrial Health Consultants |
- Industrial Safety/Health Consultants
Experts in safety/health diagnoses and guidance at workplaces
- Upon registration with the Minister of Health, Labour and Welfare, industrial
safety consultants and industrial health consultants are experts who diagnose
workplaces at the request of employers and provide guidance on the basis
of such diagnoses in order to improve industrial safety or industrial health
standards at workplaces. These consultants are required to have not only
high expertise in industrial safety and health, but also well-developed
guidance skills supported by extensive experience and a strong interest
in safety and health.
- Specialty areas for industrial safety consultant examinations include machinery, electricity, chemistry, building and civil engineering. Those for industrial health consultant examinations include health preservation, and industrial hygiene engineering. These examinations include both paper and oral tests.
(Major Requirements for Test Taking)
- (1) Industrial safety consultant examinations
 Those who have graduated in the sciences from universities and with five
years or more of experience in practical work related to safety. Those who have graduated in the sciences from universities and with five
years or more of experience in practical work related to safety.
 Those who have graduated in the sciences from junior colleges or senior
technical colleges and with seven years or more of experience in practical
work related to safety. Those who have graduated in the sciences from junior colleges or senior
technical colleges and with seven years or more of experience in practical
work related to safety.
 Those who have graduated in the sciences from high schools and with ten
years or more of experience in practical work related to safety. Those who have graduated in the sciences from high schools and with ten
years or more of experience in practical work related to safety.
(2) Industrial health consultant examinations
 Those who have graduated in the sciences from universities and with five years or more of experience in practical work related to health. Those who have graduated in the sciences from universities and with five years or more of experience in practical work related to health.
 Those who have graduated in the sciences from junior colleges or senior technical colleges and with seven years or more of experience in practical work related to health. Those who have graduated in the sciences from junior colleges or senior technical colleges and with seven years or more of experience in practical work related to health.
 Those who have graduated in the sciences from high schools and with ten years or more of experience in practical work related to health. Those who have graduated in the sciences from high schools and with ten years or more of experience in practical work related to health.
|
|

